Cutting Cycle-In-Depth Guide
Cutting Cycle-In-Depth Guide

In the intricate world of bodybuilding, achieving a chiseled physique involves not only building muscle mass but also sculpting it to reveal definition and leanness. This is where the cutting cycle comes into play. In this comprehensive Cutting Cycle-In-Depth Guide, we will explore the intricacies of cutting cycles, the science behind them, effective strategies, and considerations to ensure a successful and sustainable cutting phase.
Understanding Cutting Cycles
What is a Cutting Cycle?
A cutting cycle, often referred to as "cutting," is a phase in bodybuilding during which the primary goal is to reduce body fat while preserving lean muscle mass. This is typically done after a bulking phase, where the focus is on building muscle through a caloric surplus.
Key Objectives:
The key objectives of a cutting cycle include:
a. Fat Loss:
The primary goal is to shed excess body fat to reveal muscle definition and achieve a lean physique.
b. Muscle Preservation:
While losing fat, it's crucial to preserve lean muscle mass to maintain strength and aesthetics.
c. Maintaining Energy Levels:
Despite being in a caloric deficit, it's essential to optimize energy levels to support workouts and overall well-being.
d. Nutrient Timing:
Careful manipulation of nutrient intake, particularly carbohydrates and fats, to support energy needs and enhance fat metabolism.
The Science Behind Cutting Cycles
Caloric Deficit:
The fundamental principle of cutting is creating a caloric deficit, where the body expends more calories than it consumes. This deficit is necessary for the breakdown of stored fat to be used as an energy source.
Macronutrient Balance:
While in a caloric deficit, maintaining an appropriate balance of macronutrients (protein, carbohydrates, and fats) is crucial. Protein intake is particularly important to preserve lean muscle mass.
Nutrient Timing:
Timing nutrient intake around workouts, known as nutrient timing, can optimize energy levels and enhance fat burning. Consuming carbohydrates before and after workouts supports energy needs, while adequate protein intake helps with muscle repair and recovery.
Cardiovascular Exercise:
Cardiovascular exercise is a valuable tool during cutting cycles. It increases calorie expenditure, supports cardiovascular health, and aids in fat loss. However, the type, duration, and intensity of cardio should be tailored to individual preferences and goals.
Effective Strategies for Cutting Cycles
Establish a Realistic Caloric Deficit:
Determine a moderate caloric deficit that allows for sustainable fat loss without compromising muscle mass. A deficit of 500 to 700 calories per day is generally considered safe and effective.
Prioritize Protein Intake:
Protein is essential for muscle preservation during a cutting cycle. Aim for a protein intake of 1.6 to 2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight. Lean protein sources include chicken, turkey, fish, eggs, and plant-based options like tofu and legumes.
Strategic Carbohydrate and Fat Intake:
While in a caloric deficit, it's important to strategically manage carbohydrate and fat intake. Prioritize complex carbohydrates and healthy fats to support energy needs. Consider adjusting carbohydrate intake around workouts to optimize performance.
Implement High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT):
HIIT is a time-efficient and effective cardiovascular exercise method that involves short bursts of intense activity followed by periods of rest. It enhances calorie burning, metabolic rate, and cardiovascular fitness.
Weight Training Emphasis:
Resistance training remains a cornerstone of cutting cycles. Focus on compound movements and maintain intensity to preserve muscle mass. Adequate protein intake and progressive overload are essential for muscle maintenance and growth.
Stay Hydrated:
Adequate hydration is crucial for overall health and can support the body's metabolic processes. Drinking water before meals can also contribute to a feeling of fullness, potentially reducing overall calorie intake.
Monitor Progress and Adjust:
Regularly assess progress through measurements, body fat percentages, and visual cues. Adjust the caloric intake, macronutrient distribution, and exercise routine based on progress and individual responses.
Considerations and Tips
Gradual Changes:
Make gradual adjustments to caloric intake and exercise routines to prevent drastic changes that may compromise muscle mass or overall well-being.
Cheat Meals:
Incorporating occasional cheat meals can provide psychological relief and help prevent feelings of deprivation. However, moderation is the key to avoid undermining progress.
Sufficient Sleep:
Quality sleep is essential for recovery and hormonal balance. Aim for 7-9 hours of sleep per night to support overall health and optimize the benefits of a cutting cycle.
Supplementation:
Consider incorporating supplements that support fat loss and muscle preservation, such as branched-chain amino acids (BCAAs), omega-3 fatty acids, and thermogenic supplements (when appropriate).
Consultation with Professionals:
Before embarking on a cutting cycle, especially for those with underlying health conditions, it's advisable to consult with healthcare professionals or registered dietitians. They can provide personalized guidance based on individual needs and goals.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
Excessive Caloric Restriction:
Severely restricting calories can lead to muscle loss, nutrient deficiencies, and a slowed metabolism. Aim for a moderate deficit that supports fat loss while preserving muscle mass.
Overreliance on Cardio:
While cardiovascular exercise is valuable, overreliance on excessive cardio can lead to muscle loss and increased stress on the body. A balanced approach that includes resistance training is essential.
Neglecting Protein Intake:
Inadequate protein intake can compromise muscle preservation. Prioritize protein-rich foods and, if necessary, consider protein supplementation to meet daily requirements.
Skipping Resistance Training:
Neglecting resistance training can result in muscle loss during a cutting phase. Maintain a consistent weight training routine to support muscle maintenance and growth.
Ignoring Nutrient Timing:
Timing nutrient intake around workouts is crucial for optimizing energy levels and supporting muscle preservation. Neglecting nutrient timing can compromise performance and recovery.
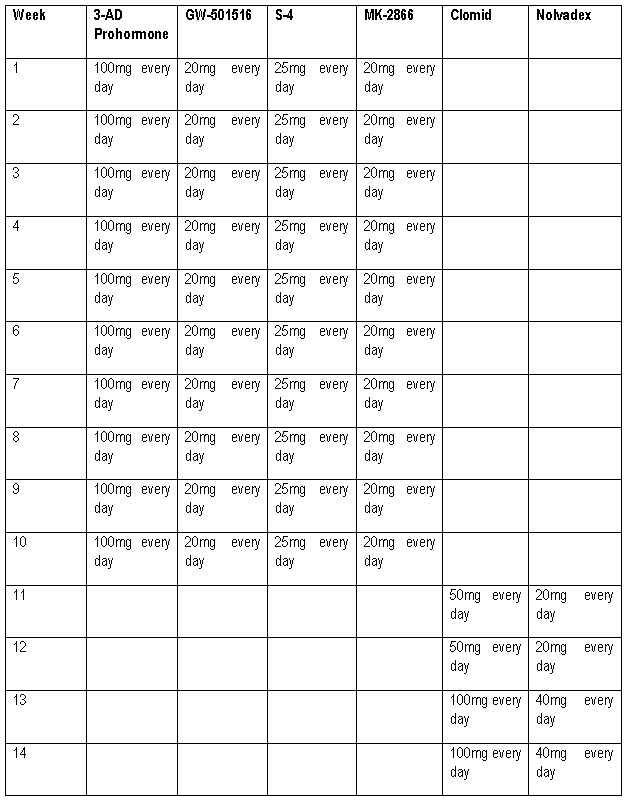
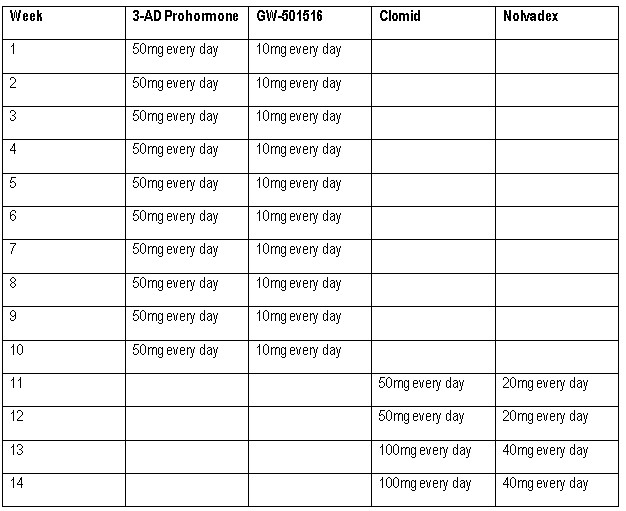
Cycles For Men
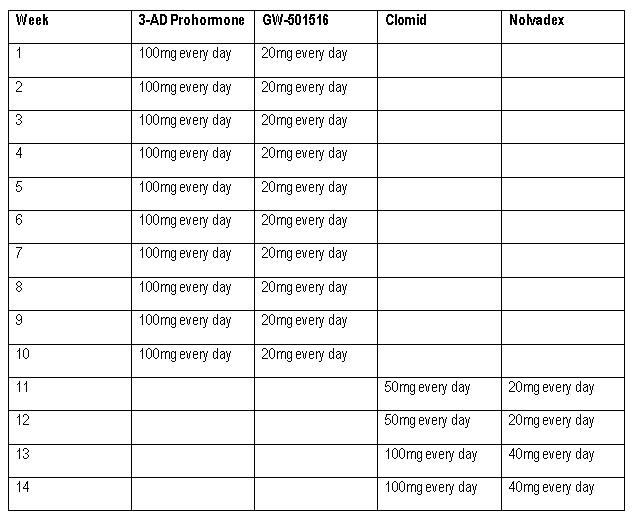
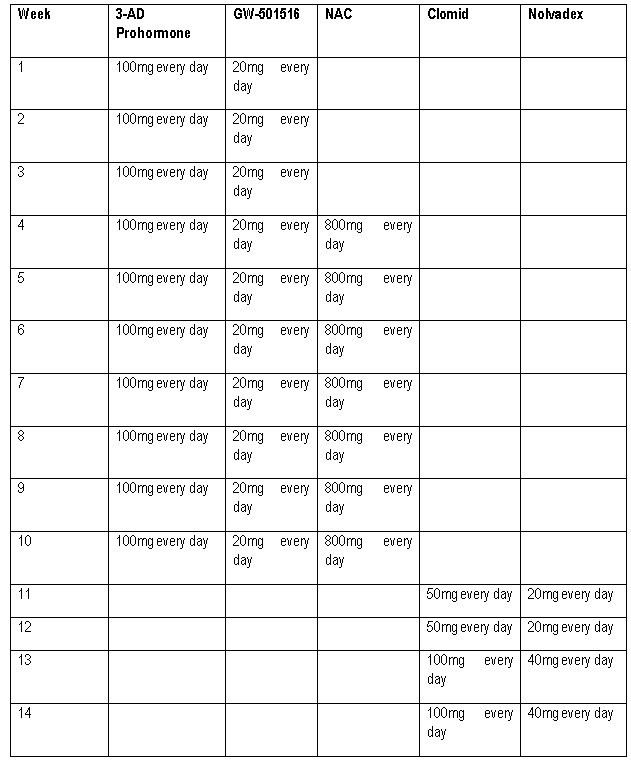
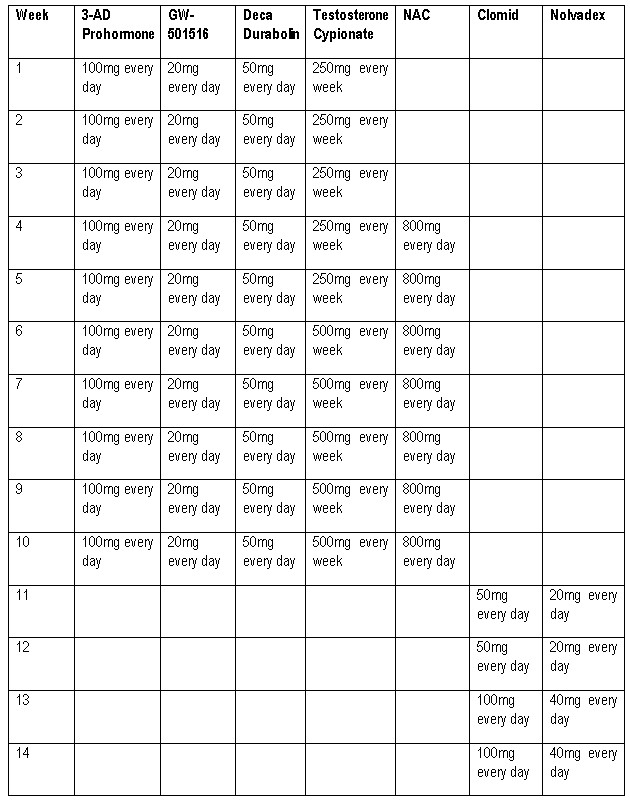
Cycles For Women
Conclusion
Embarking on a cutting cycle is a strategic and disciplined approach to achieving a lean and defined physique in bodybuilding. By understanding the science behind cutting cycles, implementing effective strategies, and considering individual needs, bodybuilders can successfully navigate this phase while preserving hard-earned muscle mass. As with any aspect of fitness, a balanced and sustainable approach is the key to long-term success. Remember, the journey to a sculpted physique is a marathon, not a sprint, and mastering the cut requires patience, dedication, and a well-informed plan.
We hope that this Cutting Cycle-In-Depth Guide was useful to you.
Recommended product - Magnus Ostarine (MK-2866)