Fueling the Gains - A Comprehensive Guide to Bulking Foods
Fueling the Gains-A Comprehensive Guide to Bulking Foods
For those on the journey to building muscle mass and achieving a robust physique, the significance of proper nutrition cannot be overstated. The process of "bulking" involves consuming a surplus of calories to support muscle growth and strength gains. In this detailed blog post, we will explore the fundamentals of bulking, the importance of the right macronutrients, and a comprehensive list of bulking foods to fuel your gains effectively.
Understanding Bulking
Caloric Surplus:
Bulking requires a caloric surplus, meaning you consume more calories than your body expends. This surplus provides the extra energy needed for muscle growth, repair, and overall performance during intense workouts.
Macronutrient Distribution:
While the overall caloric intake is crucial during a bulking phase, the distribution of macronutrients plays a significant role. Protein, carbohydrates, and fats are the building blocks of a successful bulking diet, each serving a specific purpose in supporting muscle growth.
Progressive Overload:
To stimulate muscle growth, it's essential to engage in progressive overload, gradually increasing the intensity of your workouts. The combination of a caloric surplus and progressive overload creates an optimal environment for muscle hypertrophy.
Bulking Foods: The Essentials
Lean Protein Sources
Protein is paramount for muscle repair and growth. Opt for lean protein sources to minimize excess fat intake:
a. Chicken Breast:
A versatile and lean protein source, chicken breast is rich in amino acids essential for muscle protein synthesis.
b. Turkey:
Similar to chicken, turkey provides lean protein and is a great alternative for variety in your diet.
c. Fish (Salmon, Tuna):
Fatty fish like salmon provide omega-3 fatty acids alongside high-quality protein, supporting overall health and muscle growth.
d. Eggs:
Eggs are a complete protein source, containing all essential amino acids. Additionally, they provide healthy fats and various vitamins.
e. Greek Yogurt:
Greek yogurt is not only rich in protein but also contains probiotics that support gut health.
Complex Carbohydrates
Carbohydrates are the body's primary energy source, crucial for intense workouts and overall performance.
a. Sweet Potatoes:
Packed with complex carbohydrates, sweet potatoes provide sustained energy and are rich in vitamins and minerals.
b. Brown Rice:
An excellent source of complex carbohydrates, brown rice also offers fiber, promoting digestive health.
c. Quinoa:
Quinoa is a complete protein source and contains complex carbohydrates, making it a versatile and nutritious option.
d. Oats:
Oats are high in fiber and provide a steady release of energy, making them an ideal breakfast or pre-workout option.
e. Whole Wheat Pasta:
A staple in many bulking diets, whole wheat pasta offers complex carbohydrates for sustained energy.
Healthy Fats
While controlling overall fat intake is crucial, incorporating healthy fats is essential for hormone production and overall health.
a. Avocado:
Rich in monounsaturated fats, avocados provide a creamy texture and a nutrient boost to meals.
b. Nuts (Almonds, Walnuts):
Nuts are calorie-dense and offer a mix of healthy fats, protein, and essential vitamins.
c. Olive Oil:
Extra virgin olive oil is a heart-healthy source of monounsaturated fats, perfect for cooking and dressing salads.
d. Fatty Fish (Salmon, Mackerel):
Beyond being a protein source, fatty fish provide omega-3 fatty acids, supporting overall health.
Dairy and Alternatives
Dairy products and alternatives contribute to overall macronutrient intake, offering a mix of protein, carbohydrates, and fats.
a. Milk:
Whole milk provides a balance of protein, carbohydrates, and fats, making it a calorie-dense option.
b. Cheese:
Cheese adds flavor and texture to meals, offering protein and healthy fats.
c. Cottage Cheese:
Cottage cheese is rich in protein and can be a versatile addition to both savory and sweet dishes.
d. Plant-Based Alternatives (Almond Milk, Soy Milk):
For those opting for plant-based choices, almond milk and soy milk provide a mix of macronutrients.
Vegetables and Fruits
While not calorie-dense, vegetables and fruits offer essential vitamins, minerals, and fiber crucial for overall health.
a. Broccoli:
Broccoli is a nutrient-dense vegetable that adds volume to meals without a significant increase in calories.
b. Spinach:
Spinach is rich in iron, vitamins, and minerals, providing a nutritional boost.
c. Bananas:
Bananas offer a quick source of energy and are a convenient addition to smoothies or snacks.
d. Berries (Blueberries, Strawberries):
Berries are rich in antioxidants and can add sweetness to meals without excessive calories.
e. Oranges:
Oranges provide vitamin C and natural sugars, offering a refreshing and nutritious snack.
Incorporating Bulking Foods into Your Diet
Meal Planning
Plan your meals to ensure you are meeting your caloric and macronutrient goals. This helps maintain consistency and facilitates effective tracking.
Pre- and Post-Workout Nutrition
Prioritize nutrient-dense meals around your workouts to fuel your body adequately and support recovery.
Smart Snacking
Incorporate snacks between meals to meet your caloric needs and provide sustained energy throughout the day. Nutrient-dense snacks can include Greek yogurt, nuts, or a piece of fruit.
Hydration
Stay well-hydrated to support overall health and aid digestion. Water is essential for nutrient absorption and helps regulate body temperature during intense workouts.
Supplements
While whole foods should form the foundation of your diet, supplements can be used strategically to fill nutritional gaps. Protein supplements, for example, can be convenient for meeting daily protein requirements.
Considerations
Monitoring Progress
Regularly assess your progress by tracking changes in strength, muscle mass, and overall body composition. Adjust your caloric intake based on your goals and how your body responds.
Balanced Approach
While the goal is to consume a caloric surplus, avoid excessive overeating, as it can lead to unwanted fat gain. Aim for a gradual and controlled increase in calories.
Individual Variability
Each individual's response to bulking foods can vary. Pay attention to how your body reacts to different foods and adjust your diet accordingly.
Professional Guidance
Consult with healthcare professionals, nutritionists, or fitness experts to create a personalized bulking plan tailored to your specific needs and goals.
Cycles For Men
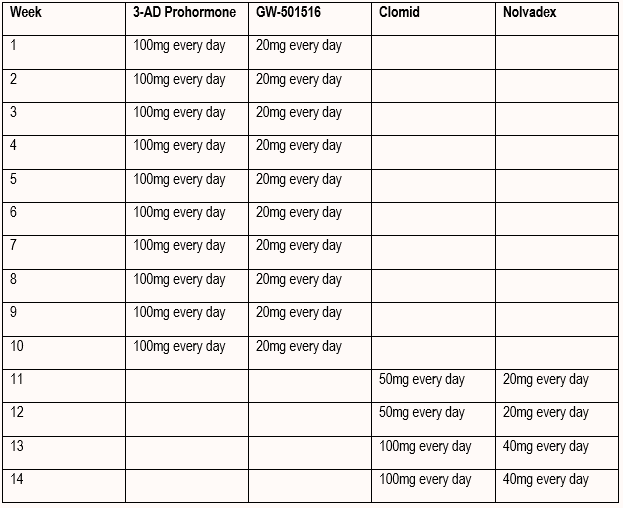
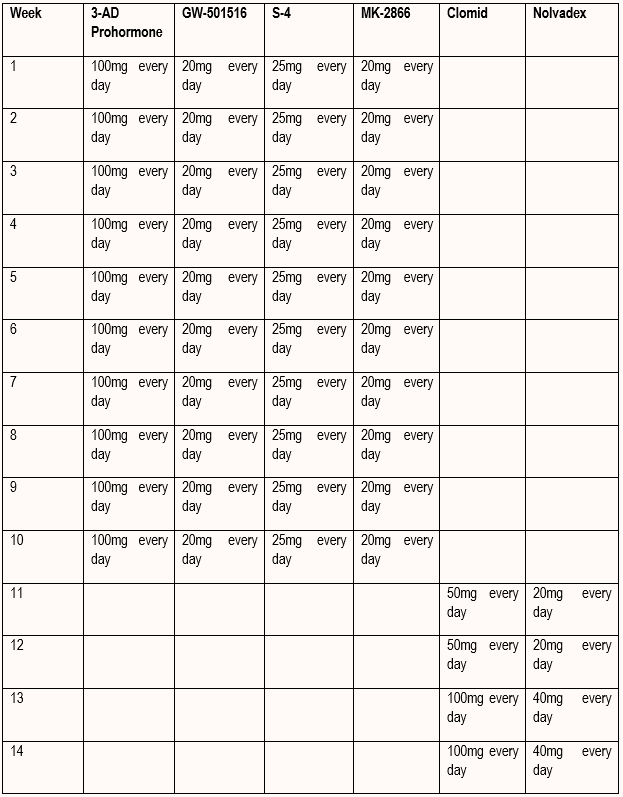
Conclusion
Embarking on a bulking journey requires a combination of dedication, proper training, and a well-designed nutrition plan. By incorporating the right balance of macronutrients from a variety of foods, you can surely pursue your journey of a healthy you in the best possible way.
Recommended product - Kevin Levrone Anabolic Mass 3kg







